HPV
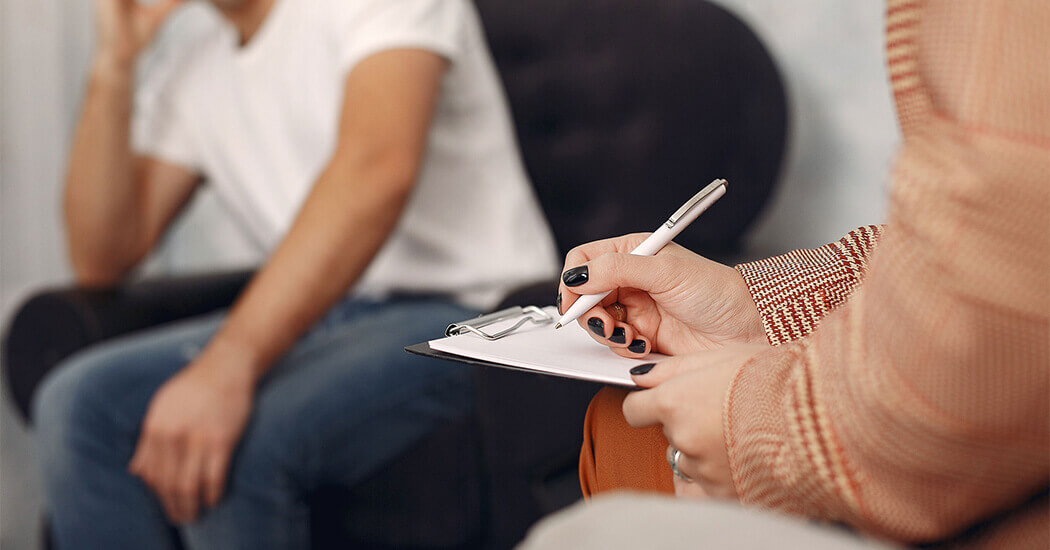
Genital warts (condylomas) are a symptom of a viral disease that is seen due to the human papilloma virus (HPV) in the genital areas of both male and female individuals. These warts have a cauliflower-like appearance and a miscellaneous shape. This condition is observed in 1% of the US population and typically around the ages of 20 to 30. Genital warts diagnosed in male individuals are very significant in terms of community healthcare and must be treated. It is a sexually transmitted infection that can be transmitted even without complete sexual intercourse. The incubation period of this disease varies. Symptoms might be seen months or years after contracting the virus. Sometimes, the virus might remain dormant, and the individual becomes a carrier without showing any symptoms. The virus might spread to other areas while shaving the genital area. Therefore, warts that were a few in number before might become much more abundant by spreading fast around the area. In men, lesions on the genital area are typically 2-10 mm in diameter. They are seen mostly on the preputium (foreskin), frenulum (sensitive area right under the penile glans), mons pubis (seen in the figure), coronal sulcus (sulcus on the penile glans), scrotum, groins and anus. It is rarely seen on the urethra (urethra and bladder). In women, it might appear on the vulva, cervix, within the vagina, urethra, bladder and anus. Genital warts can be treated with interventional and non-interventional methods.