Labiaplasty
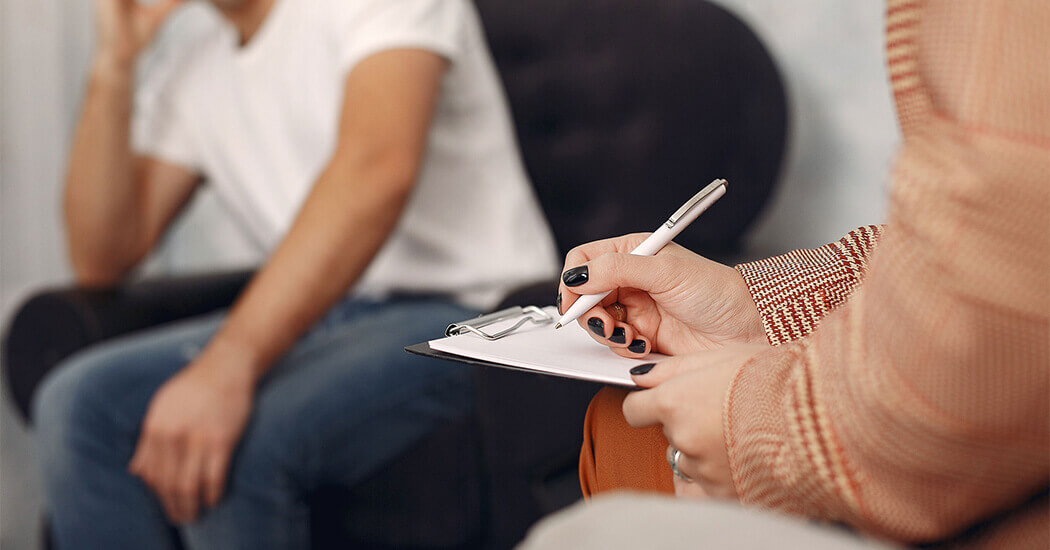
The labia minora are elastic structures that start in between the larger vulval lips (labia majora) from the level of the clitoris (the area of sexual pleasure area) at the top of the vulva and end below the entry of the vagina. Their size varies from person to person. In some women, they are larger than usual due to hormonal changes during puberty, and they protrude. They might grow in ptotic, symmetrical or asymmetrical ways. The reason for this growth is usually structural, and it might also occur at later stages. Labia minora that are overgrown might block the vagina and the urinary canal called the urethra. They might cause infections both in the vagina and in the urinary tract by creating a moist zone. Additionally, problems such as a foul smell, hygienic problems due to the sweating of the labia minora, as well as dryness, scratchiness and irritation due to contact with underwear, might occur. Larger labia minora might make the entry of the penis into the vagina more difficult during intercourse.
Considering all these problems that may affect both the woman and her sexual partner, this condition can be fixed through a simple surgical procedure. Such labia minora can be brought to the desired appearance with the operation called labiaplasty. This operation takes around half an hour and can be applied in combination with other genital aesthetic procedures. Three to four weeks of resting would be required before taking part in active sexual life.
Labiaplasty surgeries, which do not involve any danger if performed by specialist physicians in genital areas, may involve some risks when done by non-specialist physicians.
There is no harm in the surgery of all female individuals except for young girls under the age of 18.
Labiaplasty surgeries can be performed in approximately 30-40 minutes.
Approximately 30 days after surgery is sufficient for complete recovery.
Surgery prices vary depending on where and by whom to apply, whether there will be additional demands on the application. The healthiest price information is obtained from the physician after clinical examination.